Detecting Clickbaits (3/4) - Logistic Regression

Problem.
Given a set of 32000 headlines and their labels, whether that headline is a clickbait (label 1) or
not (label 0), you’re asked to build a model to detect clickbait headlines.
Solution.
Read data:
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.github.com/hminooei/DSbyHadi/master/data/clickbait_data.csv.zip")
df.tail(2)
df.head(2)
Split into train/validation/test sets:
text_train_val, text_test, label_train_val, label_test = train_test_split(
df["headline"],
df["clickbait"],
test_size=0.25,
stratify=df["clickbait"],
random_state=9)
# Split the train_val dataset to train and validation separete portions.
text_train, text_val, label_train, label_val = train_test_split(
text_train_val,
label_train_val,
test_size=0.2,
random_state=9)Define a function that builds a pipeline line consisting of CountVectorizer,
TfidfTransformer (note that you can combine these two and use TfidfVectorizer),
and LogisticRegression stages so that you can pass different parameters to it
for tuning:
def train_measure_model(text_train, label_train, text_val, label_val,
cv_binary, cv_analyzer, cv_ngram, cv_max_features,
cv_have_tfidf, cv_use_idf, cfr_penalty, cfr_C, stop_words=None,
text_column_name="headline"):
cv = CountVectorizer(binary=cv_binary, stop_words=stop_words,
analyzer=cv_analyzer,
ngram_range=cv_ngram[1:3],
max_features=cv_max_features)
if cv_have_tfidf:
pipeline = Pipeline(steps=[("vectorizer", cv),
("tfidf", TfidfTransformer(use_idf=cv_use_idf)),
("classifier", LogisticRegression(penalty=cfr_penalty,
C=cfr_C,
random_state=9,
max_iter=100,
n_jobs=None))])
else:
pipeline = Pipeline(steps=[("vectorizer", cv),
("classifier", LogisticRegression(penalty=cfr_penalty,
C=cfr_C,
random_state=9,
max_iter=100,
n_jobs=None))])
pipeline.fit(text_train, label_train)
print_metrics(pipeline, text_train, label_train, text_val, label_val)
return pipelinewhere the evaluation section is refactored into print_metrics:
def print_metrics(pipeline, text_train, label_train, text_val, label_val):
train_preds = pipeline.predict(text_train)
val_preds = pipeline.predict(text_val)
print("train:")
print(metrics.classification_report(label_train, train_preds, labels=[0, 1], digits=4))
print(metrics.confusion_matrix(label_train, train_preds))
print("validation:")
print(metrics.classification_report(label_val, val_preds, labels=[0, 1], digits=4))
print(metrics.confusion_matrix(label_val, val_preds))Now, we run the function with a few different parameters (we tried 4 sets) to reach the trained model below:
cfr_pipeline = train_measure_model(text_train, label_train, text_val, label_val,
cv_binary=True, cv_analyzer="word", cv_ngram=("w", 1, 3),
cv_max_features=5000, cv_have_tfidf=True, cv_use_idf=True,
cfr_penalty="l2", cfr_C=1.0, stop_words=None)which can be tested against test set:
measure_model_on_test(cfr_pipeline, text_test, label_test)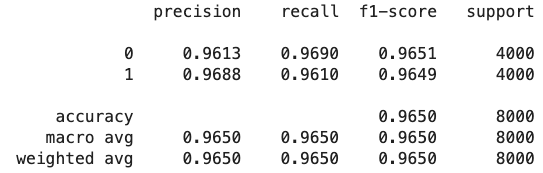
Please see the next post Detecting Clickbaits (4/4) - Manual Boosting for further improvement of this model.
Important Points.
- The training time:
1.3sper cycle (on my laptop), and since I did 4 cycles to search for parameters it took 1 minutes overall. - Macro precision on test set:
0.9650 - Inference time per record:
~1mson my laptop (MacBook Pro: 2.3 GHz 8-Core Intel Core i9, 32 GB 2667 MHz DDR4)
Note.